内存分配器
要使用UEFI固件的内存分配器,我们可以通过EFI_BOOT_SERVICES中的AllocatePool()和FreePool()函数,图6.1展示了它们的定义。
本节示例代码的目录为为malloc (日文版为050_bs_malloc)。
enum EFI_MEMORY_TYPE {
...
EfiLoaderData,
/* 已加载的UEFI应用程序的数据段,以及应用程序分配内存的默认类型 */
...
};
struct EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE {
...
struct EFI_BOOT_SERVICES {
...
// Memory Services
unsigned long long _buf3[3];
unsigned long long (*AllocatePool)(
enum EFI_MEMORY_TYPE PoolType,
/* 分配的内存类型
* 这里使用上面提到的EfiLoaderData */
unsigned long long Size,
/* 要分配的内存大小 */
void **Buffer
/* 指向已分配内存区域的指针的指针 */
);
unsigned long long (*FreePool)(
void *Buffer
/* 要释放的已分配区域的指针 */
);
...
} *BootServices;
};
图6.1: AllocatePool()和FreePool()的定义(位于efi.h中)
这里AllocatePool()函数的第一个参数分配的内存类型我们只介绍EfiLoaderData一种,在枚举EFI_MEMORY_TYPE中还定义了其他的类型。如果你想了解其它的类型,请阅读标准文档"6.2 Memory Allocation Services(P.129)"。
图6.2展示了一个使用AllocatePool()和FreePool()的例子。
#include "efi.h"
#include "common.h"
#include "graphics.h"
#define IMG_WIDTH 256
#define IMG_HEIGHT 256
void efi_main(void *ImageHandle __attribute__ ((unused)),
struct EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable)
{
unsigned long long status;
struct EFI_GRAPHICS_OUTPUT_BLT_PIXEL *img_buf, *t;
unsigned int i, j;
efi_init(SystemTable);
ST->ConOut->ClearScreen(ST->ConOut);
/* 分配图像所需要的内存空间 */
status = ST->BootServices->AllocatePool(
EfiLoaderData,
IMG_WIDTH * IMG_HEIGHT *
sizeof(struct EFI_GRAPHICS_OUTPUT_BLT_PIXEL),
(void **)&img_buf);
assert(status, L"AllocatePool");
/* 生成图像 */
t = img_buf;
for (i = 0; i < IMG_HEIGHT; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < IMG_WIDTH; j++) {
t->Blue = i;
t->Green = j;
t->Red = 0;
t->Reserved = 255;
t++;
}
}
/* 绘制图像(写入帧缓冲区) */
blt((unsigned char *)img_buf, IMG_WIDTH, IMG_HEIGHT);
/* 释放先前分配的内存 */
status = ST->BootServices->FreePool((void *)img_buf);
assert(status, L"FreePool");
while (TRUE);
}
图6.2: 使用AllocatePool()和FreePool()的例子
上面这段代码分配了一段255x255像素大小的内存区域,在这块内存区域写入像素信息,并使用blt()函数将其写入帧缓冲区使其显示在屏幕上。
这里绘制的是以蓝色为x轴,绿色为y轴的色阶图,每个轴上有256级,如图6.3所示。
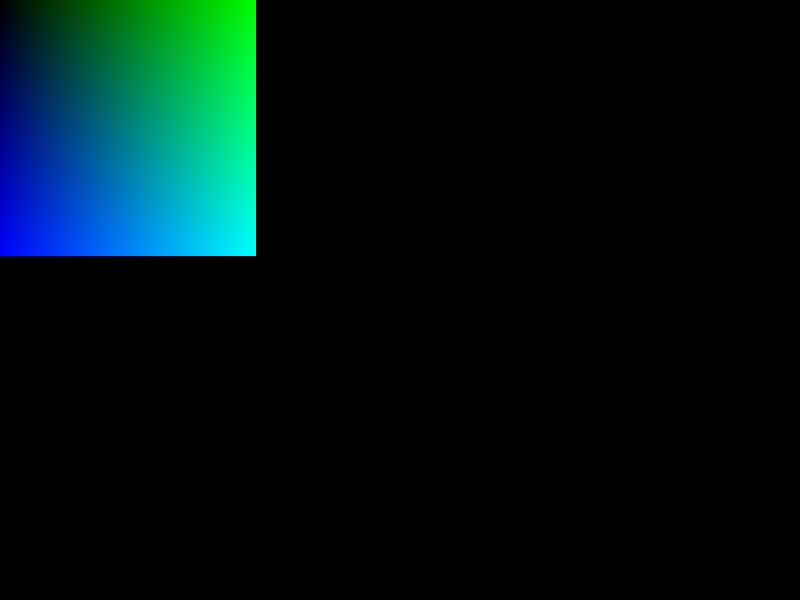
图6.3: 绘制的蓝-绿色阶图